China Accelerates Development of Reusable Rocket Technology to Strengthen Its Global Space Ambitions
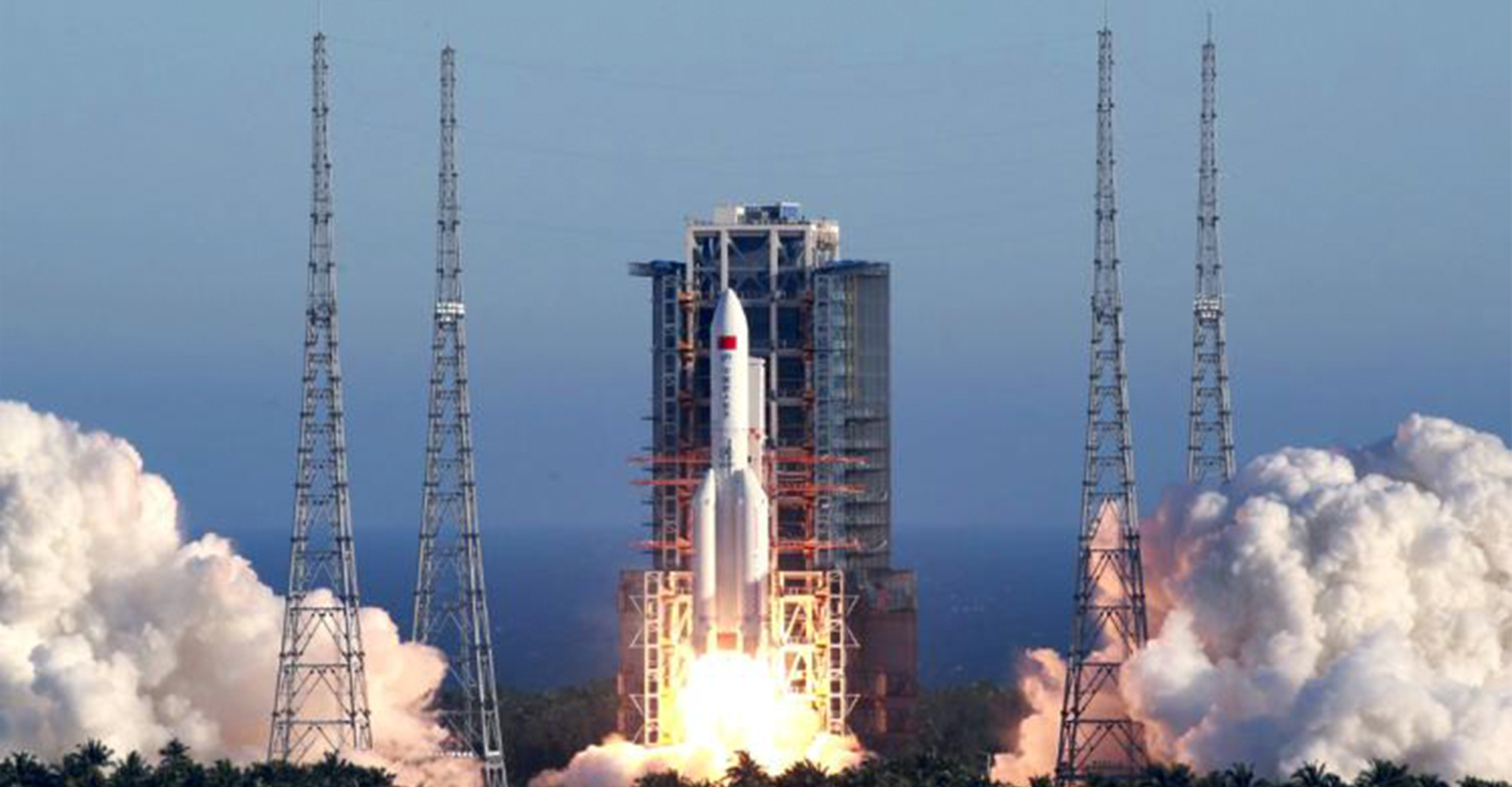

China is rapidly advancing the development of reusable rocket technology, with several large-scale rocket models expected to conduct launch missions as early as 2026. This strategic push marks a significant step in Beijing’s broader ambition to compete more directly with leading space powers and to reshape the global space technology landscape.
Reusable rocket technology, long viewed as a game-changing innovation in the space sector, offers substantial advantages in terms of cost reduction, launch frequency, and operational flexibility. By enabling rockets or key components to be recovered and reused after launch, space agencies and private companies can dramatically lower the cost of access to space. China’s accelerated investment in this field signals its determination to narrow the technological gap with established leaders such as the United States.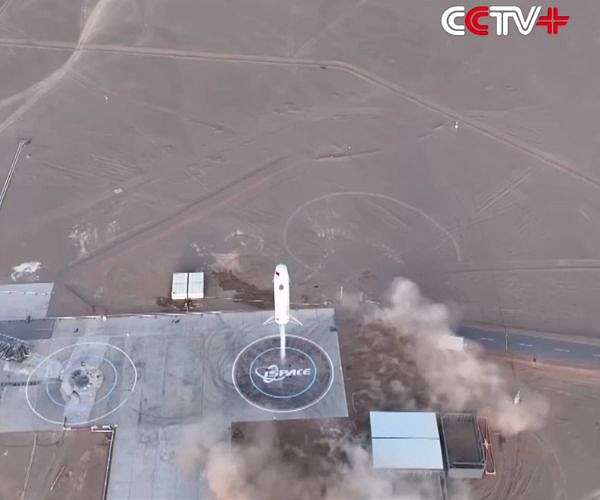
According to Chinese aerospace experts and state-backed research institutions, the upcoming generation of reusable rockets will feature larger payload capacities and more advanced recovery systems than previous experimental models. These rockets are designed to support a wide range of missions, including satellite deployment, space station resupply, deep-space exploration, and potential commercial launches for international clients.
The planned launches in 2026 are widely seen as a crucial milestone. Successful missions would demonstrate China’s ability to master complex technologies such as precision landing, reusable propulsion systems, and rapid turnaround operations. These capabilities are considered essential for building a sustainable and competitive space launch ecosystem in the long term.
Beyond technological prestige, China’s focus on reusable rockets carries significant strategic implications. Space is increasingly recognized as a critical domain for national security, economic development, and scientific leadership. Reusable launch systems could enhance China’s capacity to deploy satellites more quickly and efficiently, strengthening its position in areas such as communications, navigation, Earth observation, and space-based services.
The development effort also reflects China’s evolving space industry model. In recent years, Beijing has encouraged greater participation from commercial space companies alongside traditional state-owned aerospace enterprises. Several Chinese private firms are reportedly involved in reusable rocket research, contributing to a more dynamic and competitive domestic space sector.
Internationally, China’s progress is expected to intensify global competition in space technology. As more countries pursue reusable launch systems, the space domain is becoming more crowded and technologically complex. Analysts note that this trend could accelerate innovation but also raise new concerns related to space governance, orbital congestion, and the long-term sustainability of space activities.
Despite the ambitious timeline, significant challenges remain. Developing reliable reusable rockets requires extensive testing, substantial financial investment, and a high tolerance for risk. Technical setbacks and delays are common in advanced aerospace programs, and Chinese engineers will need to overcome these hurdles to meet their 2026 launch goals.
Nevertheless, China’s determination to advance reusable rocket technology underscores its broader vision of becoming a leading space power. As the race for space innovation intensifies, the success or failure of China’s upcoming reusable rocket launches could have far-reaching implications for the future of global space competition and cooperation.